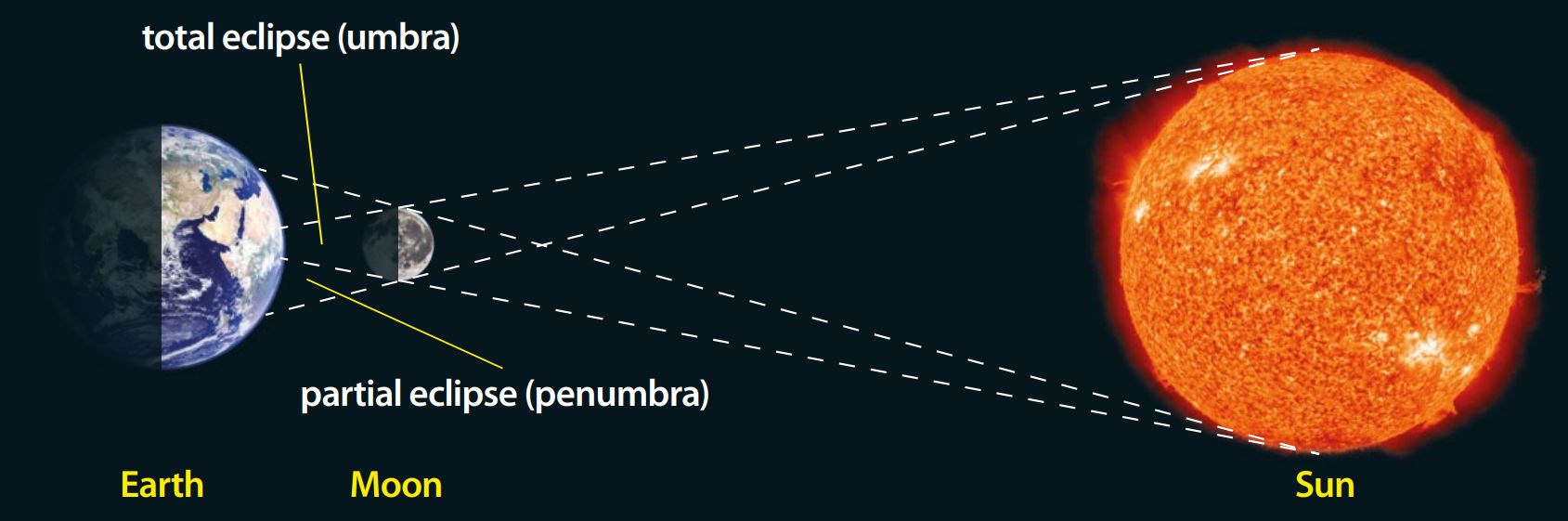
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun.
A total solar eclipse occurs when the path of the Moon produces a relatively small area of shadow on the Earth known as the “umbra”, where it completely covers the face of the Sun. The view of a solar eclipse from this area is quite spectacular. The Moon completely covers the face of the Sun as its distance and size just happens to be in the same proportions as that of the Sun.
